SEO Power Play: Chapter 3.5 – On-Page SEO Optimization
Table of Contents
Introduction
In today’s digital age, images are a fundamental part of websites, social media platforms, and digital marketing campaigns. They add visual appeal, help convey information, and enhance user experience. However, images that are not optimized can severely affect website performance, slow down page loading times, and increase bounce rates. As more users access websites on mobile devices and expect fast load times, image optimization becomes crucial in delivering an optimal experience.
Image optimization refers to the process of reducing image file sizes while maintaining the visual quality of the images. Optimizing images improves website loading speed, reduces bandwidth usage, enhances SEO, and boosts user experience. In this article, we will discuss the importance of image optimization, best practices, tools for image optimization, and how it impacts SEO and user engagement.
With optimized images, websites not only perform better but also rank higher on search engines, such as Google, which factors loading time and user experience into their ranking algorithms. We will delve into the techniques and tools that ensure your images are optimized for both speed and quality.
What is Image Optimization?
Image optimization refers to the process of reducing an image’s file size without sacrificing its quality. This process is essential for ensuring that images on your website load quickly, which is crucial for retaining visitors and ensuring a seamless browsing experience. It involves several key strategies:
- Compression: This refers to the process of reducing the size of the image by eliminating unnecessary data. Compression can be lossy, which reduces file size by removing some data (which may reduce quality), or lossless, where data is preserved but optimized for file size reduction.
- Resizing: Images that are larger than they need to be for a specific webpage should be resized. For instance, a 4000×3000 pixel image might be resized to 800×600 pixels to match the required dimensions, which reduces file size without compromising on display quality.
- File Format Adjustments: Different image formats have different compression methods, and selecting the right format can have a significant impact on optimization. Common formats include JPEG, PNG, and WebP.
For a deeper understanding, you can explore resources on image optimization on platforms like Wikipedia for more background on the subject.
Why is Image Optimization Important?
The need for image optimization is heightened by the growing importance of fast-loading websites. The speed of your website impacts user retention, bounce rates, and SEO. Images that are too large will slow down the load time of your pages, which can hurt your website’s overall performance and ranking.
Understanding Image File Formats

To effectively optimize images, it’s important to choose the right file format for the right purpose. The format you choose can influence the file size and quality of an image. Below is an explanation of the most common image file formats used in image optimization:
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
JPEG is a widely used format for photos and images with many colors. It employs lossy compression, meaning some image quality is lost during compression to reduce the file size. However, the loss is often imperceptible to the human eye.
- Advantages: Smaller file sizes and good for images with subtle color changes (e.g., photographs).
- Disadvantages: Lossy compression can reduce image quality if over-compressed.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
PNG is a lossless format, meaning that it does not lose any data during compression. This makes it suitable for images that need transparency or sharp edges, like logos, icons, or infographics.
- Advantages: Lossless compression, supports transparency, and retains high-quality details.
- Disadvantages: Larger file sizes compared to JPEG, not ideal for complex images or photos.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
GIF is commonly used for animations and simple graphics. It supports up to 256 colors and works well for images that don’t require too much detail or color depth. GIF is often used for small, simple graphics or animated images.
- Advantages: Ideal for animations and small graphics.
- Disadvantages: Limited color palette makes it unsuitable for detailed or photo-realistic images.
WebP (Web Picture Format)
WebP, developed by Google, provides superior compression compared to JPEG and PNG. It supports both lossy and lossless compression and also supports transparency, making it an excellent choice for web images.
- Advantages: Smaller file sizes, supports transparency, both lossy and lossless compression.
- Disadvantages: Limited browser support, but this is quickly improving.
AVIF (AV1 Image File Format)
AVIF is a relatively new format that uses advanced compression algorithms to create high-quality images at smaller file sizes. AVIF is expected to be the future of image optimization, offering superior quality with reduced sizes.
- Advantages: Excellent compression, supports HDR, smaller file sizes, and high-quality images.
- Disadvantages: Limited browser support, though adoption is increasing.
Best Practices for Image Optimization

Image optimization is a multi-step process that involves resizing, compressing, and selecting the appropriate file format for each image. Below are some of the best practices to follow:
Resizing Images for Web Usage
One of the most important aspects of image optimization is resizing. Many images are uploaded to websites at resolutions that are much higher than necessary. For example, an image displayed at 800×600 pixels may have originally been uploaded at 4000×3000 pixels, which unnecessarily increases file size.
By resizing images to fit the exact display size on your website, you can significantly reduce their file size. Tools like Adobe Photoshop, GIMP, and online platforms like TinyPNG can be used to resize images without affecting quality.
Choosing the Right File Format
Choosing the right file format is critical for image optimization. Depending on the type of image, certain formats will be better than others:
- JPEG is ideal for photographs or images with complex gradients.
- PNG is the best choice for images with transparency, like logos or icons.
- WebP is great for reducing file size without losing quality and works well for a wide variety of images.
For a detailed understanding of how to choose the right format, visit resources like Wikipedia on Image Compression.
Compression Techniques and Their Effects
Compression is the most effective way to reduce file size without compromising quality. Compression can be either lossy or lossless:
- Lossy compression works by removing some of the image data to reduce the file size. While this may lead to some loss of quality, the reduction in file size can be significant.
- Lossless compression, on the other hand, retains all of the image data and reduces file size by optimizing it. This technique is useful when image quality is crucial.
Using compression tools like TinyPNG, Squoosh, and ImageOptim can help find the right balance between file size and quality. These tools automatically apply the most appropriate compression methods based on the image type and your quality preferences.
Implementing Lazy Loading
Lazy loading is a technique that defers the loading of images until they are needed. Rather than loading all images on a page when it first loads, lazy loading loads them as the user scrolls down the page. This reduces the initial load time, saves bandwidth, and improves page performance.
Lazy loading is particularly useful on websites with a large number of images, like e-commerce sites or news websites.
Responsive Image Optimization
With an increasing number of users accessing websites on mobile devices, responsive images have become essential. Responsive images automatically adjust their size based on the user’s device, ensuring optimal quality and performance. The srcset and sizes attributes in HTML allow developers to serve different image sizes depending on the device’s screen resolution and size.
By using responsive images, you can ensure that mobile users do not have to download unnecessarily large images, which helps to reduce loading times and data consumption.
Tools and Software for Image Optimization

Several tools can assist with image optimization, making it easier to resize, compress, and convert images for web use. Here are some popular tools:
Image Optimization Software
- Adobe Photoshop: This is a comprehensive tool for image editing and optimization. Photoshop provides a range of options for resizing, compressing, and saving images in different formats.
- GIMP: A free, open-source alternative to Photoshop, GIMP offers similar features for image resizing, cropping, and optimization.
- Affinity Photo: An affordable alternative to Photoshop, Affinity Photo offers a wide range of image optimization features at a lower cost.
Online Image Optimization Tools
- TinyPNG: TinyPNG is a free, easy-to-use online tool that can compress PNG and JPEG files while retaining good quality.
- Squoosh: Developed by Google, Squoosh is an online tool that allows you to compress images in real-time and convert them into various formats, including WebP.
- ImageOptim: Available for macOS, ImageOptim is a tool that provides lossless image compression to reduce file size without sacrificing quality.
Automated Image Optimization with CDNs
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) like Cloudflare and KeyCDN can help automate image optimization. These services offer on-the-fly optimization of images, automatically serving the most appropriate image formats (like WebP) based on the user’s browser and device. This ensures that images are always optimized for performance without requiring manual intervention.
Image Optimization and SEO
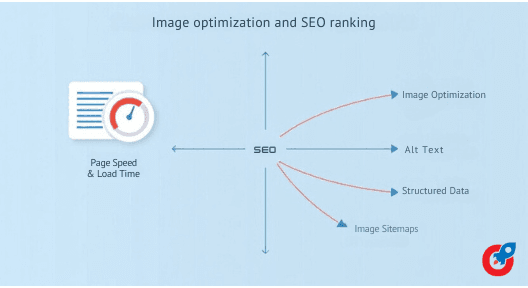
Images play a significant role in SEO, as search engines consider website loading speed, user experience, and accessibility when determining rankings. Image optimization can improve SEO in several ways:
SEO Benefits of Image Optimization
Optimized images contribute to faster load times, which is a key factor in search engine rankings. A faster website provides a better user experience
, leading to lower bounce rates and higher user engagement. Search engines like Google use page load times as a ranking factor, so optimizing images can help your website rank higher in search results.
Alt Text for Image Optimization
Alt text, or alternative text, describes the content of an image and is used by search engines to index images properly. It also helps users with visual impairments understand the content of the image. Writing descriptive alt text that includes relevant keywords can improve SEO and help your images appear in Google Image Search.
Structured Data and Image Sitemaps
Using structured data, like Schema.org markup, can provide search engines with additional information about your images, such as the type of image or its relevance to the page content. Including images in your XML sitemap also helps search engines crawl and index your images more effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, image optimization is an essential practice for improving website performance, enhancing SEO, and providing an optimal user experience. By following best practices, using the right tools, and selecting appropriate image formats, you can ensure that your website loads faster, uses less bandwidth, and ranks higher in search engines. As the web continues to evolve, embracing new formats like WebP and AVIF will further improve image optimization, offering better compression and faster load times.
For more detailed information on optimizing images and their impact on SEO, you can refer to resources such as Wikipedia on Image Compression.
By implementing the techniques and strategies discussed in this article, you can ensure that your website is optimized for speed, performance, and search engine visibility, ultimately leading to better user engagement and higher conversion rates.

